Cost optimization is critical in manufacturing procurement. Companies must balance quality, supplier relationships, and operational efficiency while keeping costs under control. However, many businesses struggle with procurement inefficiencies due to outdated budgeting methods.
Zero-Based Budgeting (ZBB) offers a strategic approach to managing procurement expenses. Unlike traditional budgeting, which relies on past expenditures, ZBB requires every cost to be justified from scratch. This method eliminates unnecessary spending, improves cost visibility, and aligns procurement with business objectives.
As procurement costs rise due to fluctuating raw material prices and supply chain disruptions, manufacturing companies must adopt efficient budgeting practices. ZBB provides a disciplined and data-driven approach, helping businesses make informed purchasing decisions and drive profitability.
Traditional Budgeting vs. Zero-Based Budgeting in Procurement
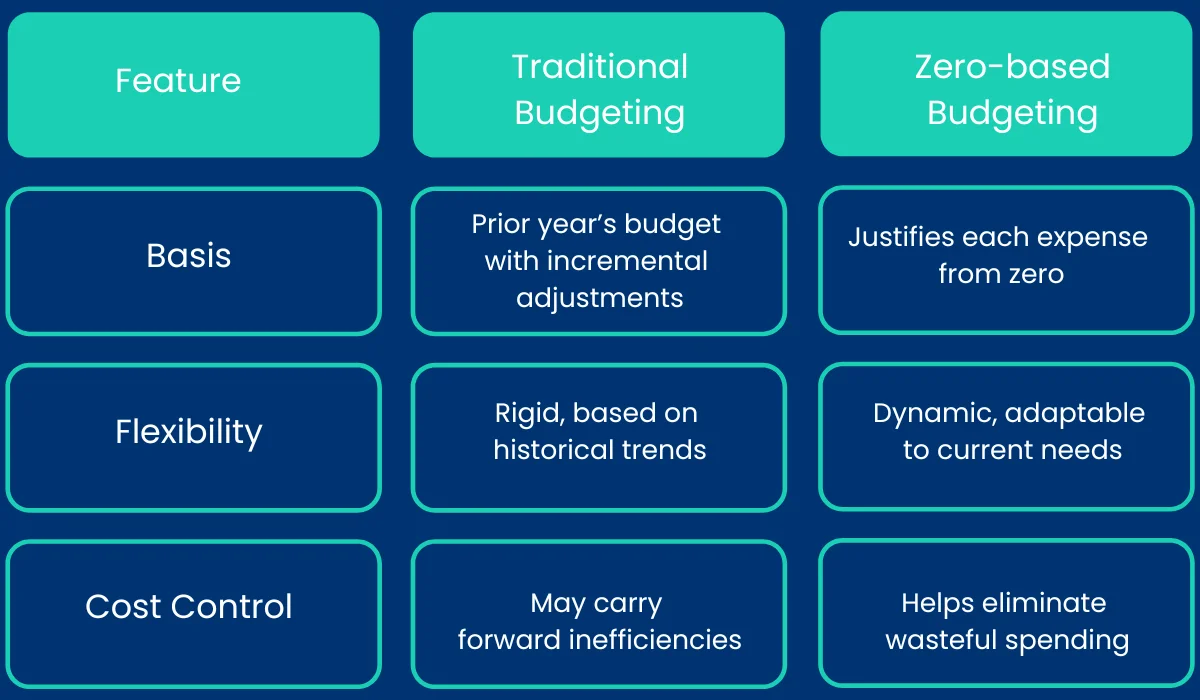
Traditional Budgeting
Traditional budgeting follows a predictable pattern. Companies take the previous year’s procurement budget, adjust it for inflation or expected cost changes, and use it as a baseline for the next period. While this method offers stability, it often carries forward inefficiencies.
Zero-Based Budgeting (ZBB)
ZBB takes a completely different approach. Instead of relying on past budgets, every procurement expense is assessed from the ground up. This method ensures that each cost is necessary and justified based on current business needs.
Key Principles of ZBB
- All costs require proper justification to be included. People working in procurement teams need to prove the reason for every budget request because they cannot expect funding through automatic channels. All organizational costs must prove their value toward achieving business objectives.
- The budget creation process under ZBB aligns with company objectives instead of following previous budget data. The technique cuts costs from operations that are irrelevant to the current strategy.
- Each procurement cost undergoes a thorough cost-benefit analysis system for measuring return on investment (ROI) results. Budget optimization through this method stops excessive spending and allows money to be invested for the highest return on value creation.
- For classification purposes, budgeted expenses are divided into two essential and non-essential groups. The system of categorization enables procurement teams to separate essential expenses from those that might be optimized and removed from their operations.
- Procurement teams need to research each budgeted resource to eliminate expenses from unnecessary duplicate acquisitions and services.
Also Read: Procurement vs. Purchasing
Importance of ZBB in Procurement

1. Enhancing Cost Control
The lack of proper oversight causes procurement teams to experience difficulties with excessive spending. ZBB brings complete transparency to organizations while enabling them to eliminate unnecessary spending. Businesses analyze existing needs instead of allowing earlier ineffectiveness to persist across operations. Procurement professionals get complete and accurate expenditure control through the ZBB application, thus delivering funds to the most critical areas.
2. Eliminating Budgetary Waste
The standard procurement budget contains expenses that repeat themselves without necessity. An organization will keep buying supplies that have lost their original usefulness at levels from previous years. ZBB enables organizations to analyze every procurement decision, thus avoiding flawed resource distribution and guaranteeing crucial supply and service acquisition using available funds. Through this method, organizations can prevent themselves from maintaining assumptions about constant procurement requirements.
3. Improving Financial Discipline
With ZBB, organizations do not approve expenses based on past trends. Instead, they assess procurement costs with a fresh perspective, fostering a culture of accountability and financial discipline. Every department must justify its spending requests, making budget planning more precise and results-driven.
4. Aligning Procurement with Business Objectives
Multiple procurement budgets show continuous expansion because they lack proper strategic alignment with key organizational goals. The ZBB approach provides organizations with the risk management tool to guarantee their investment dollars generate increased business achievements and operational optimization. For example, a manufacturing company shifts its buying funds from non-crucial office materials to purchase higher-quality raw materials that enhance product standards.
5. Supporting Data-Driven Decision Making
The ZBB process compels organizations to use data instead of subjective assumptions when making choices. Procurement teams base their purchasing decisions on the results of controller-based cost-benefit analysis. Proper data analysis helps businesses uncover their cost-reduction potential while granting them better capabilities to negotiate contracts and optimize their relationships with vendors.
Also Read: Manufacturing Cost vs Production Cost
Implementing Zero-Based Budgeting in Procurement

Step 1: Define Budgeting Objectives
Organizations need to specify their exact targets before starting with ZBB implementation. Common goals may include:
- Cost reduction without compromising quality
- Better supply chain efficiency results from optimized business procedures.
- Procurement should work towards achieving business growth and innovation targets.
- Business profitability benefits from eliminating all unneeded costs.
Step 2: Identify Cost Categories
The total procurement expenses are broken down into diverse sections.
The categories of necessary expenses include those that sustain business operations, such as raw materials, IT infrastructure, and supply chain logistical needs.
At the same time, Discretionary Costs represent optional operational expenses, which include office furniture modifications and corporate event organization.
The company should eliminate costs that offer minimum value to business operations, such as redundant software license agreements and inactive subscriptions.
Step 3: Evaluate Existing Expenses
Organizations need to study their previous budget patterns before establishing new financial forecasting. This process reveals business areas and monetary savings possibilities within the organization. Procurement teams need to examine previously made transactions to determine how each purchase impacts operational efficiency.
Step 4: Justify Every Expense
Procurement teams must explain the validity of all business expenses. Justifications should include:
- Business necessity and operational impact
- Expected return on investment (ROI)
- Compliance with regulatory or company policies
- Potential cost savings or efficiency improvements
Step 5: Prioritize Spending
The worth of procurement expenses may vary greatly from one expense to another. Organizations need to establish spending areas of highest priority according to measurable effects. Essential purchases, such as raw materials for production, take precedence over discretionary or non-essential costs. Decision-makers need to examine costs that enhance revenue performance and customer satisfaction.
Step 6: Monitor and Adjust
Once a ZBB plan is in place, the execution needs ongoing evaluation. Organizations need methods to observe their spending patterns and results, which leads them to modify their budgets. The evaluation process lets procurement teams improve their budget creation methods while keeping costs efficient.
Challenges of Zero-Based Budgeting in Procurement
Time-Consuming Process
A complete examination and supporting evidence are mandatory for every procurement cost under ZBB. The procedure demands substantial effort, particularly when organizations are large. Evaluation of past spending and the creation of new budgetary plans by procurement teams need time.
Resistance to Change
Employees and stakeholders who have worked with traditional budgeting systems often demonstrate opposition to the implementation of ZBB. The process demands appropriate teaching and team message distribution as basic requirements for obtaining workers’ agreement. Leadership must stress the approach’s long-term advantages to improve acceptance.
Complexity in Large Organizations
Large organizations with many procurement departments will face additional challenges when they choose to deploy ZBB throughout their business operations. Implementing procurement technology helps simplify budgeting operations to address these obstacles.
Need for Accurate Data
ZBB relies on accurate financial data. Weak or faulty input data will cause decision-making to become inaccurate. Organizations performing procurement should utilize dependable analytic systems that protect data reliability.
Best Practices for Effective ZBB Implementation

1. Use Technology and Automation
Procurement software and data analytics tools make implementing ZBB processes easier. The automated tracking system reduces worker input while providing more exact information. AI-driven procurement systems for businesses make evaluating supplier costs and streamlining purchasing decisions possible.
2. Engage Key Stakeholders
ZBB systems need active partnership among procurement staff, financial teams, and those who make organizational decisions. A harmonious transition occurs when all involved parties receive proper alignment. A clear dialogue about cost distribution with proper explanations stops stakeholders from developing wrong interpretations.
3. Focus on Value, Not Just Cost-Cutting
The goal of ZBB is not just to reduce costs but to optimize spending. Businesses should focus on investments that drive long-term value. Cutting costs in essential areas may lead to lower quality products or services, which can harm the company in the long run.
4. Implement Gradually
Instead of a company-wide overhaul, organizations can introduce ZBB in phases. Starting with high-spend areas allows teams to refine the process before full adoption. A phased approach minimizes disruptions and helps teams adapt.
5. Regularly Review and Adapt
The business environment and market variables change continuously. Cursory assessments of ZBB strategies must occur periodically to maintain budget effectiveness. Such regular evaluations help organizations make ongoing cost improvements.
Conclusion
Zero-based budgeting in procurement helps businesses eliminate waste, enhance financial discipline, and align spending with business objectives. While it requires effort and planning, the long-term benefits outweigh the challenges. By implementing best practices and leveraging technology, organizations can optimize procurement budgets and drive cost efficiency. ZBB is a strategic approach that fosters smarter financial decision-making and sustainable growth.





