The clock is ticking fast, and auto manufacturers who don’t adopt the latest trends in automotive industry will fail quickly and be left behind. The first one to lead the future of the automotive industry is electric vehicles. By 2030, around 30% of the new vehicle sales in the country will be fully electric. Well, EVs alone won’t drive the future. Autonomous driving technology and AI will have their fair share and shape customers’ expectations.
This blog delves into recent trends in automobile industry that matter the most today and tomorrow, focusing on how they will transform production, cost calculation, and consumer demand.
9 Current Trends in the Automobile Industry
1. Electric Vehicle Production Will Take the Steering Wheel
EV adoption is accelerating globally, with regional variations influenced by government incentives, infrastructure, and consumer behavior. For instance, Norway leads with over 80% of new car sales being EVs, while countries like India are focusing on affordable EV options to cater to cost-sensitive consumers. Addressing challenges such as rare earth material sourcing for batteries and recycling solutions will also be crucial for the future of EVs.
2. Autonomous Driving Technology Rethinking the Designing
Self-driving vehicles are not only reshaping design but also creating new regulatory challenges. As countries develop standards for autonomous vehicle (AV) testing and deployment, manufacturers must balance innovation with compliance. Public perception and trust in AV safety remain critical barriers, necessitating education campaigns and transparent reporting on safety data.
3. Connected Car Technology Will Enter the Production
The connected car market is rapidly evolving, integrating IoT and advanced telematics. These features enhance vehicle diagnostics, enable over-the-air updates, and provide real-time traffic management. However, cybersecurity threats are emerging as a significant concern, requiring manufacturers to invest in robust data protection measures and regulatory compliance.
4. 3D Printing Will Accelerate Production
Manufacturers will have to accelerate production to meet the demands and remain competitive. However, rapidly producing autonomous or electric vehicles will be a challenge. Trial and error will prove more risky.
From designing a prototype and estimating manufacturing costs to final production, manufacturers cannot take risks at any stage. It would also impact the profits and sustainability efforts.
3D printing will address these challenges and enable manufacturers to produce prototypes faster than now. Even the complex components can be printed with 3D technology, reducing time, cost, effort, and waste.
Additionally, it will help experiment with lightweight and durable materials that can be used to develop fuel-efficient vehicles.
5. Advanced Robotics Will Optimize Production Lines
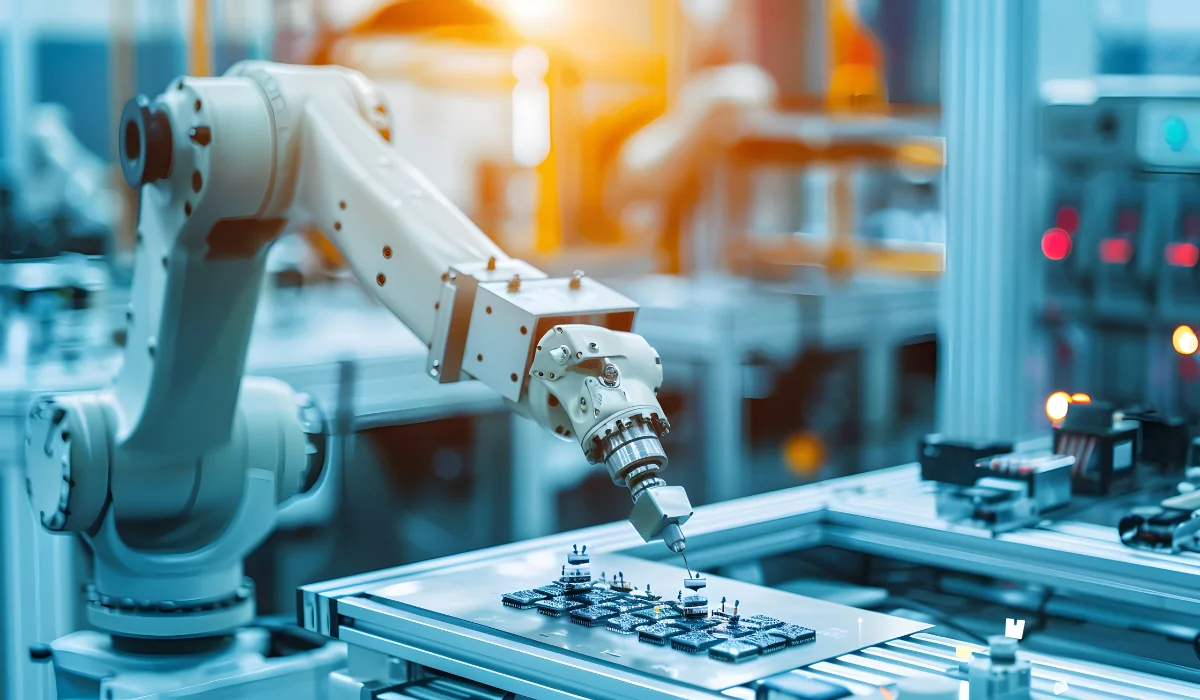
Robotics powered by AI is optimizing production lines, but its impact on the workforce must not be overlooked. As repetitive tasks become automated, the demand for skilled workers in robotics programming and maintenance will rise. Manufacturers need to prioritize reskilling programs to ensure a smooth transition for workers and maintain social equity.
6. Automation to Accelerate Speed and Precision
Automation has already begun but will achieve new heights, increasing efficiency on the production floor. From assembly lines to control systems, automation will expand everywhere, allowing manufacturers to scale production.
It will double the throughput and reduce human errors. Furthermore, automation will be a key driver of cost reduction for manufacturers.
7. AI in Automotive Manufacturing
AI is transforming automotive manufacturing through predictive analytics, reducing waste, and enhancing efficiency. Machine learning (ML) and computer vision technologies are advancing quality control by detecting micro-defects invisible to the human eye. Examples include Tesla’s AI-driven supply chain system, which predicts disruptions and ensures timely part availability.
8. Machine Learning Improving Quality Control in Production
Sustainability is more than reducing carbon footprints—it involves a holistic approach to resource efficiency. Initiatives like closed-loop recycling, renewable energy adoption, and biodegradable materials are gaining traction. Case in point: Volvo aims to become carbon neutral by 2040 by using 25% recycled plastics and reducing lifecycle emissions.
9. Sustainable Manufacturing in the Automotive Industry
While EVs and AVs dominate today’s trends, emerging technologies like hydrogen fuel cells, quantum computing, and vehicle-to-grid (V2G) integration will define the next wave. Quantum computing could revolutionize battery optimization and material science, while V2G systems allow EVs to act as energy storage, stabilizing grids during peak demand. Additionally, sustainable manufacturing in the automotive industry will play a crucial role in ensuring these advancements are both eco-friendly and efficient.
Regional and Consumer-Centric Focus
Automotive industry trends vary widely based on geography and consumer demographics:
- Asia: Growth in shared mobility services and affordable EV models.
- Europe: Stringent emissions regulations and high EV adoption.
- North America: Emphasis on AVs and connected car technologies. Understanding these distinctions allows manufacturers to tailor strategies to specific markets.
Challenges and Opportunities in the Supply Chain
The global supply chain faces challenges from rare earth shortages for EV batteries to semiconductor scarcity. Manufacturers must explore alternative materials, diversify supply chains, and invest in domestic production capabilities. Collaborative partnerships across industries will be essential for resilience.
Bridging the Skills Gap
The rapid shift to automation and AI highlights the need for workforce transformation. Governments and manufacturers must collaborate on training initiatives, including apprenticeships and online learning platforms, to prepare workers for the future of automotive industry.
Conclusion
The automotive industry is on the cusp of transformative change, with innovations shaping vehicles and how they are produced and experienced. Future automotive technology and trends shaping the future of automotive industry will redefine how manufacturers operate. Manufacturers embracing sustainability, leveraging cutting-edge technologies, and addressing workforce and consumer needs will lead the industry into the next era. The time to act is now.





